Data Wrangling
Download the PDF of the presentation
This tutorial has been forked from awesome classes developed by Adam Wilson here: http://adamwilson.us/RDataScience/
The R Script associated with this page is available here. Download this file and open it (or copy-paste into a new script) with RStudio so you can follow along.
1 RStudio Shortcuts
1.1 Running code
ctrl-R(orcommand-R) to run current line- Highlight
codein script and runctrl-R(orcommand-R) to run selection - Buttons:

1.2 Switching windows
ctrl-1: script windowctrl-2: console window
Try to run today’s script without using your mouse/trackpad
2 Data wrangling
2.1 Useful packages: dplyr and tidyr
Cheat sheets on website for Data Wrangling
library(dplyr)
library(tidyr)Remember use install.packages("dplyr") to install a new package.
2.1.1 Example operations from here
2.2 New York City Flights
Data from US Bureau of Transportation Statistics (see ?nycflights13)
library(nycflights13)Check out the flights object
head(flights)## # A tibble: 6 × 19
## year month day dep_time sched_dep_time
## <int> <int> <int> <int> <int>
## 1 2013 1 1 517 515
## 2 2013 1 1 533 529
## 3 2013 1 1 542 540
## 4 2013 1 1 544 545
## 5 2013 1 1 554 600
## 6 2013 1 1 554 558
## # ... with 14 more variables: dep_delay <dbl>,
## # arr_time <int>, sched_arr_time <int>,
## # arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
## # tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>,
## # air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>,
## # minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>2.2.1 Object Structure
Check out data structure with glimpse()
glimpse(flights)## Observations: 336,776
## Variables: 19
## $ year <int> 2013, 2013, 2013, 2013...
## $ month <int> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1...
## $ day <int> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1...
## $ dep_time <int> 517, 533, 542, 544, 55...
## $ sched_dep_time <int> 515, 529, 540, 545, 60...
## $ dep_delay <dbl> 2, 4, 2, -1, -6, -4, -...
## $ arr_time <int> 830, 850, 923, 1004, 8...
## $ sched_arr_time <int> 819, 830, 850, 1022, 8...
## $ arr_delay <dbl> 11, 20, 33, -18, -25, ...
## $ carrier <chr> "UA", "UA", "AA", "B6"...
## $ flight <int> 1545, 1714, 1141, 725,...
## $ tailnum <chr> "N14228", "N24211", "N...
## $ origin <chr> "EWR", "LGA", "JFK", "...
## $ dest <chr> "IAH", "IAH", "MIA", "...
## $ air_time <dbl> 227, 227, 160, 183, 11...
## $ distance <dbl> 1400, 1416, 1089, 1576...
## $ hour <dbl> 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 5, 6, 6...
## $ minute <dbl> 15, 29, 40, 45, 0, 58,...
## $ time_hour <dttm> 2013-01-01 05:00:00, ...3 dplyr “verbs”
select()andrename(): Extract existing variablesfilter()andslice(): Extract existing observationsarrange()distinct()mutate()andtransmute(): Derive new variablessummarise(): Change the unit of analysissample_n()andsample_frac()
3.1 Useful select functions
- “
-” Select everything but - “
:” Select range contains()Select columns whose name contains a character stringends_with()Select columns whose name ends with a stringeverything()Select every columnmatches()Select columns whose name matches a regular expressionnum_range()Select columns named x1, x2, x3, x4, x5one_of()Select columns whose names are in a group of namesstarts_with()Select columns whose name starts with a character string
3.1.1 select() examples
Select only the year, month, and day columns:
select(flights,year, month, day)## # A tibble: 336,776 × 3
## year month day
## <int> <int> <int>
## 1 2013 1 1
## 2 2013 1 1
## 3 2013 1 1
## 4 2013 1 1
## 5 2013 1 1
## 6 2013 1 1
## 7 2013 1 1
## 8 2013 1 1
## 9 2013 1 1
## 10 2013 1 1
## # ... with 336,766 more rows3.1.2 select() examples
Select everything except the tailnum:
select(flights,-tailnum)## # A tibble: 336,776 × 18
## year month day dep_time sched_dep_time
## <int> <int> <int> <int> <int>
## 1 2013 1 1 517 515
## 2 2013 1 1 533 529
## 3 2013 1 1 542 540
## 4 2013 1 1 544 545
## 5 2013 1 1 554 600
## 6 2013 1 1 554 558
## 7 2013 1 1 555 600
## 8 2013 1 1 557 600
## 9 2013 1 1 557 600
## 10 2013 1 1 558 600
## # ... with 336,766 more rows, and 13 more
## # variables: dep_delay <dbl>, arr_time <int>,
## # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>,
## # carrier <chr>, flight <int>, origin <chr>,
## # dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>,
## # hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>Select all columns containing the string "time":
select(flights,contains("time"))## # A tibble: 336,776 × 6
## dep_time sched_dep_time arr_time
## <int> <int> <int>
## 1 517 515 830
## 2 533 529 850
## 3 542 540 923
## 4 544 545 1004
## 5 554 600 812
## 6 554 558 740
## 7 555 600 913
## 8 557 600 709
## 9 557 600 838
## 10 558 600 753
## # ... with 336,766 more rows, and 3 more
## # variables: sched_arr_time <int>,
## # air_time <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>You can also rename columns with select()
select(flights,year,carrier,destination=dest)## # A tibble: 336,776 × 3
## year carrier destination
## <int> <chr> <chr>
## 1 2013 UA IAH
## 2 2013 UA IAH
## 3 2013 AA MIA
## 4 2013 B6 BQN
## 5 2013 DL ATL
## 6 2013 UA ORD
## 7 2013 B6 FLL
## 8 2013 EV IAD
## 9 2013 B6 MCO
## 10 2013 AA ORD
## # ... with 336,766 more rows3.2 filter() observations
Filter all flights that departed on on January 1st:
filter(flights, month == 1, day == 1)## # A tibble: 842 × 19
## year month day dep_time sched_dep_time
## <int> <int> <int> <int> <int>
## 1 2013 1 1 517 515
## 2 2013 1 1 533 529
## 3 2013 1 1 542 540
## 4 2013 1 1 544 545
## 5 2013 1 1 554 600
## 6 2013 1 1 554 558
## 7 2013 1 1 555 600
## 8 2013 1 1 557 600
## 9 2013 1 1 557 600
## 10 2013 1 1 558 600
## # ... with 832 more rows, and 14 more variables:
## # dep_delay <dbl>, arr_time <int>,
## # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>,
## # carrier <chr>, flight <int>, tailnum <chr>,
## # origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
## # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>,
## # time_hour <dttm>3.3 Base R method
This is equivalent to the more verbose code in base R:
flights[flights$month == 1 & flights$day == 1, ]## # A tibble: 842 × 19
## year month day dep_time sched_dep_time
## <int> <int> <int> <int> <int>
## 1 2013 1 1 517 515
## 2 2013 1 1 533 529
## 3 2013 1 1 542 540
## 4 2013 1 1 544 545
## 5 2013 1 1 554 600
## 6 2013 1 1 554 558
## 7 2013 1 1 555 600
## 8 2013 1 1 557 600
## 9 2013 1 1 557 600
## 10 2013 1 1 558 600
## # ... with 832 more rows, and 14 more variables:
## # dep_delay <dbl>, arr_time <int>,
## # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>,
## # carrier <chr>, flight <int>, tailnum <chr>,
## # origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
## # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>,
## # time_hour <dttm>Compare with dplyr method:
filter(flights, month == 1, day == 1)`Filter the flights data set to keep only evening flights (dep_time after 1600) in June.
filter(flights,dep_time>1600,month==6)## # A tibble: 10,117 × 19
## year month day dep_time sched_dep_time
## <int> <int> <int> <int> <int>
## 1 2013 6 1 1602 1505
## 2 2013 6 1 1602 1605
## 3 2013 6 1 1602 1610
## 4 2013 6 1 1603 1610
## 5 2013 6 1 1603 1545
## 6 2013 6 1 1605 1608
## 7 2013 6 1 1605 1600
## 8 2013 6 1 1605 1614
## 9 2013 6 1 1608 1600
## 10 2013 6 1 1609 1615
## # ... with 10,107 more rows, and 14 more
## # variables: dep_delay <dbl>, arr_time <int>,
## # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>,
## # carrier <chr>, flight <int>, tailnum <chr>,
## # origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
## # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>,
## # time_hour <dttm>3.4 Other boolean expressions
filter() is similar to subset() except it handles any number of filtering conditions joined together with &.
You can also use other boolean operators, such as OR (“|”):
filter(flights, month == 1 | month == 2)## # A tibble: 51,955 × 19
## year month day dep_time sched_dep_time
## <int> <int> <int> <int> <int>
## 1 2013 1 1 517 515
## 2 2013 1 1 533 529
## 3 2013 1 1 542 540
## 4 2013 1 1 544 545
## 5 2013 1 1 554 600
## 6 2013 1 1 554 558
## 7 2013 1 1 555 600
## 8 2013 1 1 557 600
## 9 2013 1 1 557 600
## 10 2013 1 1 558 600
## # ... with 51,945 more rows, and 14 more
## # variables: dep_delay <dbl>, arr_time <int>,
## # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>,
## # carrier <chr>, flight <int>, tailnum <chr>,
## # origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
## # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>,
## # time_hour <dttm>Filter the flights data set to keep only ‘redeye’ flights where the departure time (dep_time) is “after” the arrival time (arr_time), indicating it arrived the next day:
filter(flights,dep_time>arr_time)## # A tibble: 10,633 × 19
## year month day dep_time sched_dep_time
## <int> <int> <int> <int> <int>
## 1 2013 1 1 1929 1920
## 2 2013 1 1 1939 1840
## 3 2013 1 1 2058 2100
## 4 2013 1 1 2102 2108
## 5 2013 1 1 2108 2057
## 6 2013 1 1 2120 2130
## 7 2013 1 1 2121 2040
## 8 2013 1 1 2128 2135
## 9 2013 1 1 2134 2045
## 10 2013 1 1 2136 2145
## # ... with 10,623 more rows, and 14 more
## # variables: dep_delay <dbl>, arr_time <int>,
## # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>,
## # carrier <chr>, flight <int>, tailnum <chr>,
## # origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
## # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>,
## # time_hour <dttm>3.5 Select rows with slice():
slice(flights, 1:10)## # A tibble: 10 × 19
## year month day dep_time sched_dep_time
## <int> <int> <int> <int> <int>
## 1 2013 1 1 517 515
## 2 2013 1 1 533 529
## 3 2013 1 1 542 540
## 4 2013 1 1 544 545
## 5 2013 1 1 554 600
## 6 2013 1 1 554 558
## 7 2013 1 1 555 600
## 8 2013 1 1 557 600
## 9 2013 1 1 557 600
## 10 2013 1 1 558 600
## # ... with 14 more variables: dep_delay <dbl>,
## # arr_time <int>, sched_arr_time <int>,
## # arr_delay <dbl>, carrier <chr>, flight <int>,
## # tailnum <chr>, origin <chr>, dest <chr>,
## # air_time <dbl>, distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>,
## # minute <dbl>, time_hour <dttm>3.6 arrange() rows
arrange() is similar to filter() except it reorders instead of filtering.
arrange(flights, year, month, day)## # A tibble: 336,776 × 19
## year month day dep_time sched_dep_time
## <int> <int> <int> <int> <int>
## 1 2013 1 1 517 515
## 2 2013 1 1 533 529
## 3 2013 1 1 542 540
## 4 2013 1 1 544 545
## 5 2013 1 1 554 600
## 6 2013 1 1 554 558
## 7 2013 1 1 555 600
## 8 2013 1 1 557 600
## 9 2013 1 1 557 600
## 10 2013 1 1 558 600
## # ... with 336,766 more rows, and 14 more
## # variables: dep_delay <dbl>, arr_time <int>,
## # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>,
## # carrier <chr>, flight <int>, tailnum <chr>,
## # origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
## # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>,
## # time_hour <dttm>Base R method:
flights[order(flights$year, flights$month, flights$day), ]3.7 Descending order: desc()
arrange(flights, desc(arr_delay))## # A tibble: 336,776 × 19
## year month day dep_time sched_dep_time
## <int> <int> <int> <int> <int>
## 1 2013 1 9 641 900
## 2 2013 6 15 1432 1935
## 3 2013 1 10 1121 1635
## 4 2013 9 20 1139 1845
## 5 2013 7 22 845 1600
## 6 2013 4 10 1100 1900
## 7 2013 3 17 2321 810
## 8 2013 7 22 2257 759
## 9 2013 12 5 756 1700
## 10 2013 5 3 1133 2055
## # ... with 336,766 more rows, and 14 more
## # variables: dep_delay <dbl>, arr_time <int>,
## # sched_arr_time <int>, arr_delay <dbl>,
## # carrier <chr>, flight <int>, tailnum <chr>,
## # origin <chr>, dest <chr>, air_time <dbl>,
## # distance <dbl>, hour <dbl>, minute <dbl>,
## # time_hour <dttm>Base R method:
flights[order(desc(flights$arr_delay)), ]3.8 Distinct: Find distinct rows
distinct(
select(flights,carrier)
)## # A tibble: 16 × 1
## carrier
## <chr>
## 1 UA
## 2 AA
## 3 B6
## 4 DL
## 5 EV
## 6 MQ
## 7 US
## 8 WN
## 9 VX
## 10 FL
## 11 AS
## 12 9E
## 13 F9
## 14 HA
## 15 YV
## 16 OO3.9 Mutate: Derive new variables
Adds columns with calculations based on other columns.
Average air speed (miles/hour):
select(
mutate(flights,ave_speed=distance/(air_time/60)),
distance, air_time,ave_speed)## # A tibble: 336,776 × 3
## distance air_time ave_speed
## <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 1400 227 370.0441
## 2 1416 227 374.2731
## 3 1089 160 408.3750
## 4 1576 183 516.7213
## 5 762 116 394.1379
## 6 719 150 287.6000
## 7 1065 158 404.4304
## 8 229 53 259.2453
## 9 944 140 404.5714
## 10 733 138 318.6957
## # ... with 336,766 more rows3.10 Chaining Operations
Performing multiple operations sequentially with a pipe character
- Group by a variable
- Select some columns
- Summarize observations
- Filter by results
With temporary objects:
a1 <- group_by(flights, year, month, day)
a2 <- select(a1, arr_delay, dep_delay)## Adding missing grouping variables: `year`, `month`, `day`a3 <- summarise(a2,
arr = mean(arr_delay, na.rm = TRUE),
dep = mean(dep_delay, na.rm = TRUE))
a4 <- filter(a3, arr > 30 | dep > 30)
head(a4)## Source: local data frame [6 x 5]
## Groups: year, month [3]
##
## year month day arr dep
## <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 2013 1 16 34.24736 24.61287
## 2 2013 1 31 32.60285 28.65836
## 3 2013 2 11 36.29009 39.07360
## 4 2013 2 27 31.25249 37.76327
## 5 2013 3 8 85.86216 83.53692
## 6 2013 3 18 41.29189 30.11796If you don’t want to save the intermediate results: wrap the function calls inside each other:
filter(
summarise(
select(
group_by(flights, year, month, day),
arr_delay, dep_delay
),
arr = mean(arr_delay, na.rm = TRUE),
dep = mean(dep_delay, na.rm = TRUE)
),
arr > 30 | dep > 30
)## Adding missing grouping variables: `year`, `month`, `day`## Source: local data frame [49 x 5]
## Groups: year, month [11]
##
## year month day arr dep
## <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 2013 1 16 34.24736 24.61287
## 2 2013 1 31 32.60285 28.65836
## 3 2013 2 11 36.29009 39.07360
## 4 2013 2 27 31.25249 37.76327
## 5 2013 3 8 85.86216 83.53692
## 6 2013 3 18 41.29189 30.11796
## 7 2013 4 10 38.41231 33.02368
## 8 2013 4 12 36.04814 34.83843
## 9 2013 4 18 36.02848 34.91536
## 10 2013 4 19 47.91170 46.12783
## # ... with 39 more rowsArguments are distant from function -> difficult to read!
3.11 Chaining Operations
%>% allows you to pipe together various commands
x %>% f(y) turns into f(x, y)
So you can use it to rewrite multiple operations that you can read left-to-right, top-to-bottom:
flights %>%
group_by(year, month, day) %>%
select(arr_delay, dep_delay) %>%
summarise(
arr = mean(arr_delay, na.rm = TRUE),
dep = mean(dep_delay, na.rm = TRUE)
) %>%
filter(arr > 30 | dep > 30)## Adding missing grouping variables: `year`, `month`, `day`## Source: local data frame [49 x 5]
## Groups: year, month [11]
##
## year month day arr dep
## <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 2013 1 16 34.24736 24.61287
## 2 2013 1 31 32.60285 28.65836
## 3 2013 2 11 36.29009 39.07360
## 4 2013 2 27 31.25249 37.76327
## 5 2013 3 8 85.86216 83.53692
## 6 2013 3 18 41.29189 30.11796
## 7 2013 4 10 38.41231 33.02368
## 8 2013 4 12 36.04814 34.83843
## 9 2013 4 18 36.02848 34.91536
## 10 2013 4 19 47.91170 46.12783
## # ... with 39 more rows3.12 Analyze by group with group_by()
Perform operations by group: mean departure delay by airport (origin)
flights %>%
group_by(origin) %>%
summarise(meanDelay = mean(dep_delay,na.rm=T))## # A tibble: 3 × 2
## origin meanDelay
## <chr> <dbl>
## 1 EWR 15.10795
## 2 JFK 12.11216
## 3 LGA 10.34688Perform operations by group: mean and sd departure delay by airline (carrier)
flights %>%
group_by(carrier) %>%
summarise(meanDelay = mean(dep_delay,na.rm=T),
sdDelay = sd(dep_delay,na.rm=T))## # A tibble: 16 × 3
## carrier meanDelay sdDelay
## <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 9E 16.725769 45.90604
## 2 AA 8.586016 37.35486
## 3 AS 5.804775 31.36303
## 4 B6 13.022522 38.50337
## 5 DL 9.264505 39.73505
## 6 EV 19.955390 46.55235
## 7 F9 20.215543 58.36265
## 8 FL 18.726075 52.66160
## 9 HA 4.900585 74.10990
## 10 MQ 10.552041 39.18457
## 11 OO 12.586207 43.06599
## 12 UA 12.106073 35.71660
## 13 US 3.782418 28.05633
## 14 VX 12.869421 44.81510
## 15 WN 17.711744 43.34435
## 16 YV 18.996330 49.17227Flights from which origin airport go the farthest (on average)? Hint: Group by airport (origin) then calculate the maximum flight distance (distance).
flights %>%
group_by(origin) %>%
summarise(meanDist = mean(distance,na.rm=T))## # A tibble: 3 × 2
## origin meanDist
## <chr> <dbl>
## 1 EWR 1056.7428
## 2 JFK 1266.2491
## 3 LGA 779.8357Which destination airport (dest) is the farthest (distance) from NYC?
flights %>%
arrange(desc(distance)) %>%
select(dest,distance) %>%
slice(1)## # A tibble: 1 × 2
## dest distance
## <chr> <dbl>
## 1 HNL 4983Which airport is that?
4 Combining data sets
4.1 dplyr join methods
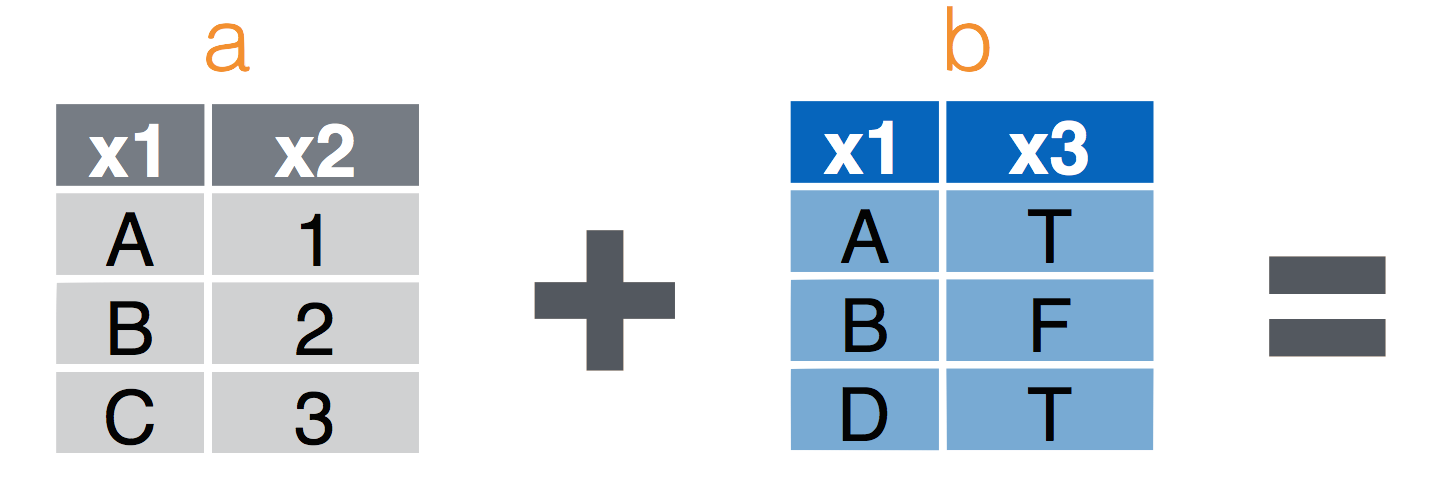
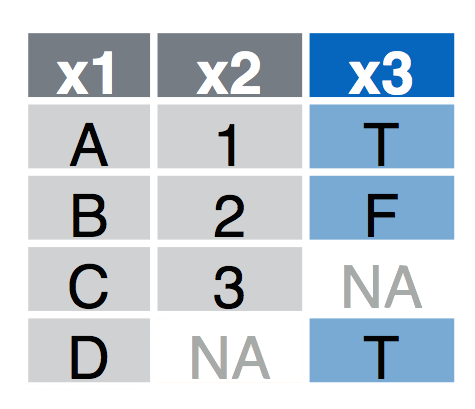
left_join(a, b, by = "x1")Join matching rows from b to a.right_join(a, b, by = "x1")Join matching rows from a to b.inner_join(a, b, by = "x1")Retain only rows in both sets.full_join(a, b, by = "x1")Join data. Retain all values, all rows.
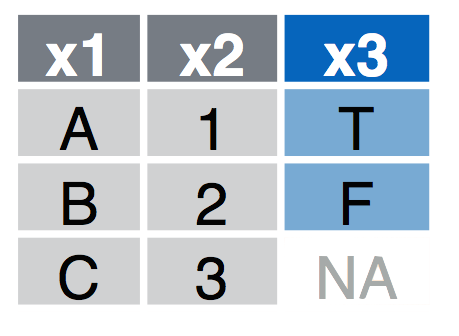
4.1.1 Left Join
left_join(a, b, by = "x1") Join matching rows from b to a.

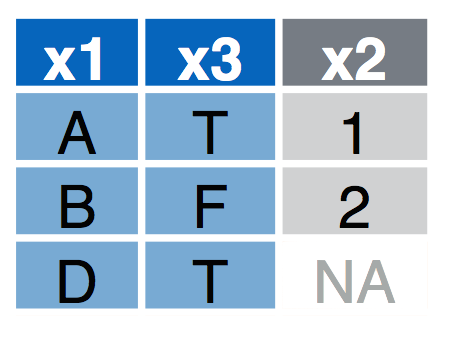
4.1.2 Right Join
right_join(a, b, by = "x1") Join matching rows from a to b.

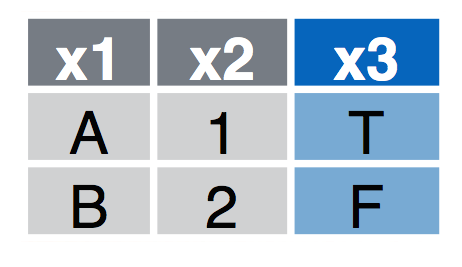
4.1.3 Inner Join
inner_join(a, b, by = "x1") Retain only rows in both sets.

4.1.4 Full Join
full_join(a, b, by = "x1") Join data. Retain all values, all rows.

flights%>%
select(-year,-month,-day,-hour,-minute,-dep_time,-dep_delay)%>%
glimpse()## Observations: 336,776
## Variables: 12
## $ sched_dep_time <int> 515, 529, 540, 545, 60...
## $ arr_time <int> 830, 850, 923, 1004, 8...
## $ sched_arr_time <int> 819, 830, 850, 1022, 8...
## $ arr_delay <dbl> 11, 20, 33, -18, -25, ...
## $ carrier <chr> "UA", "UA", "AA", "B6"...
## $ flight <int> 1545, 1714, 1141, 725,...
## $ tailnum <chr> "N14228", "N24211", "N...
## $ origin <chr> "EWR", "LGA", "JFK", "...
## $ dest <chr> "IAH", "IAH", "MIA", "...
## $ air_time <dbl> 227, 227, 160, 183, 11...
## $ distance <dbl> 1400, 1416, 1089, 1576...
## $ time_hour <dttm> 2013-01-01 05:00:00, ...Let’s look at the airports data table (?airports for documentation):
glimpse(airports)## Observations: 1,396
## Variables: 7
## $ faa <chr> "04G", "06A", "06C", "06N", "09J...
## $ name <chr> "Lansdowne Airport", "Moton Fiel...
## $ lat <dbl> 41.13047, 32.46057, 41.98934, 41...
## $ lon <dbl> -80.61958, -85.68003, -88.10124,...
## $ alt <int> 1044, 264, 801, 523, 11, 1593, 7...
## $ tz <dbl> -5, -5, -6, -5, -4, -4, -5, -5, ...
## $ dst <chr> "A", "A", "A", "A", "A", "A", "A...What is the name of the destination airport farthest from the NYC airports? Hints:
- Use a join to connect the
flightsdataset andairportsdataset. - Figure out which column connects the two tables.
- You may need to rename the column names before joining.
select(airports,
dest=faa,
destName=name)%>%
right_join(flights)%>%
arrange(desc(distance)) %>%
slice(1) %>%
select(destName)## Joining, by = "dest"## # A tibble: 1 × 1
## destName
## <chr>
## 1 Honolulu Intl4.2 Plot the flights data
The section below shows some ‘advanced’ coding to extract the geographic locations for all flights and plotting. This is just meant as an example to illustrate how one might use these functions to perform a mini-analysis that results in a map.
4.2.1 Join destination airports
library(geosphere)
library(maps)
library(ggplot2)
library(sp)
library(rgeos)## rgeos version: 0.3-21, (SVN revision 540)
## GEOS runtime version: 3.4.2-CAPI-1.8.2 r3921
## Linking to sp version: 1.2-3
## Polygon checking: TRUEdata=
select(airports,
dest=faa,
destName=name,
destLat=lat,
destLon=lon)%>%
right_join(flights)%>%
group_by(dest,
destLon,
destLat,
distance)%>%
summarise(count=n())%>%
ungroup()%>%
select(destLon,
destLat,
count,
distance)%>%
mutate(id=row_number())%>%
na.omit()## Joining, by = "dest"NYCll=airports%>%filter(faa=="JFK")%>%select(lon,lat) # get NYC coordinates
# calculate great circle routes
rts <- gcIntermediate(as.matrix(NYCll),
as.matrix(select(data,destLon,destLat)),
1000,
addStartEnd=TRUE,
sp=TRUE)## NOTE: rgdal::checkCRSArgs: no proj_defs.dat in PROJ.4 shared filesrts.ff <- fortify(
as(rts,"SpatialLinesDataFrame")) # convert into something ggplot can plot
## join with count of flights
rts.ff$id=as.integer(rts.ff$id)
gcircles <- left_join(rts.ff,
data,
by="id") # join attributes, we keep them all, just in caseNow build a basemap using data in the maps package.
base = ggplot()
worldmap <- map_data("world",
ylim = c(10, 70),
xlim = c(-160, -80))
wrld <- c(geom_polygon(
aes(long, lat, group = group),
size = 0.1,
colour = "grey",
fill = "grey",
alpha = 1,
data = worldmap
))Now draw the map using ggplot
base + wrld +
geom_path(
data = gcircles,
aes(
long,
lat,
col = count,
group = group,
order = as.factor(distance)
),
alpha = 0.5,
lineend = "round",
lwd = 1
) +
coord_equal() +
scale_colour_gradientn(colours = c("blue", "orange", "red"),
guide = "colourbar") +
theme(panel.background = element_rect(fill = 'white', colour = 'white')) +
labs(y = "Latitude", x = "Longitude",
title = "Count of Flights from New York in 2013")## Warning: Ignoring unknown aesthetics: order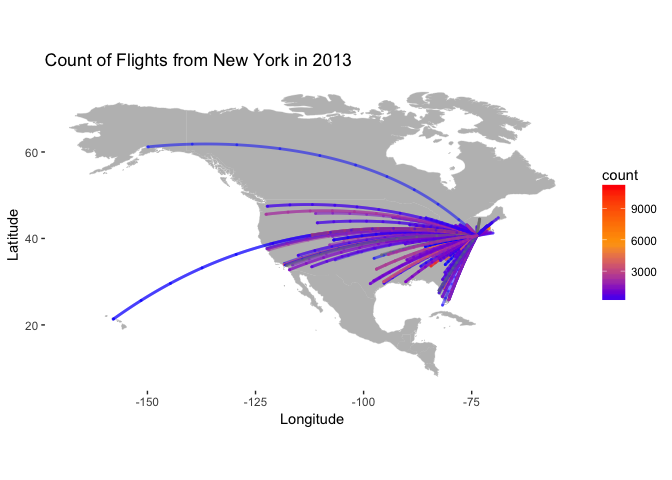
4.3 Colophon
This exercise based on code from here.